网络爬虫
requests库
request,请求,要求rəˈkwest
主要方法1
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
requests.request() | 构造一个请求,支撑以下方法 |
requests.get() | 获取HTML网页,对应HTTP中的GET |
requests.head() | 返回网页信息头的方法,对应HTTP的HEAD |
requests.post() | 向网页中提交POST的方法,对应HTTP的POST |
requests.put() | 向网页中提交PUT的方法,对应HTTP的PUT |
requests.patch() | 向网页中提交局部修改请求,对应HTTP的PATCH |
requests.delete() | 向网页中提交删除请求,对应HTTP的DELETE |
r = requests.request(请求方式,url,**kwargs)
r = requests.request("GET",url,**kwargs),与r = requests.get(URL)作用一致
get()方法
获取网页最简单的方法是变量名 = requests.get("URL")
执行过程
- 构造一个向服务器请求资源的
Request对象 - 返回一个包含服务器资源的
Response对象,包含了爬虫返回的内容,response,响应,反应,rəˈspäns
完整形式
r.get(url,params=None,**kwars)
url:获取网页的字符串链接
params:可选参数,字典或者字节流格式
**kwars:12个控制访问参数
Response的属性
| 属性 | 含义 |
|---|---|
r.status_code | 返回请求的状态,200代表成功,404表示失败 |
r.text | HTTP相应内容的字符串形式,即页面的内容(源码) |
r.encoding | 从HTTP header中猜测内容编码格式 |
r.apparent_encoding | 从内容分析编码方式 |
r.content | HTTP返回内容的二进制形式 |
- 先使用
r.get("URL")获取HTTP网页 - 使用
r.status_code查看请求的状态,200成功,其他的代表失败 - 使用
r.text获取页面内容,如果有乱码,代表r.encoding不正确,使用r.apparent_encoding的信息进行修改,最后再获取信息
通用代码框架
import requests
def getHtmlText(url):
try:
r = requests.get(url)
r.raise_for_status() # 如果状态不是200,引发HTTPError异常
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return "产生异常"
url = "http://www.baidu.com"
print(getHtmlText(url))
HTTP协议操作
| 操作 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| GET | 请求URL位置的资源,也就是把URL位置的资源拿下来 |
| HEAD | 请求URL位置资源的相应消息报告,获取头部信息,当一个资源很大不能直接拿下来,可以获取HEAD,分析其中的内容 |
| POST | 请求向URL位置的资源后附加新的数据,不改变现有URL位置的内容,只是向后新添加一个资源 |
| PUT | 请求向URL位置存储一个资源(将自己的数据放在这个位置上),原来URL位置的资源会被覆盖掉 |
| PATCH | 请求局部更新URL位置的资源,并改变该处资源的内容,比方说只修改某些数据 |
| DELETE | 删除URL位置存储的资源 |
-
获取资源可以用GET或者HEAD方法
-
把自己的数据放在相应的位置上,使用PUT、POST、PATCH
-
删除这个资源使用DELETE
-
每个操作都是独立的
-
以上的操作均与
requests库的方法一一对应
**kwargs
系统开代理,requests可能不正常!!!
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
params | 字典或者序列,增加URL中 |
data | 字典或者字节序列、对象文件,作为向服务器提交资源使用 |
json | JSON数据格式,向服务器提交内容 |
headers | 字典,HTTP定制头,也就是可以自定义UA |
cookies | 字典或者CookieJar,使用自定义cookie进行访问 |
auth | 元组,支持HTTP认证 |
files | 字典类型,向服务器传输文件使用 |
timeout | 设置超时时间,秒为单位 |
proxies | 字典类型,设置访问代理服务器,可以增加登录认证 |
allow_redirects | True/False,默认为True,重定向开关 |
stream | True/False,默认为True,获取内容立即下载开关 |
verify | True/False,默认为True,认证SSL证书的开关 |
cert | 保存本地SSL证书路径 |
params
params将字典或者序列作为参数增加到url中
import requests
url = "http://image.bloged.xyz/api/token?"
key = {"email": "邮箱", "password": "密码"}
r = requests.request(method="GET", url=url, params=key)
print(r.url)# https://image.bloged.xyz/api/token?email=邮箱&password=密码
print(r.text)# {"code":200,"msg":"success","data":{"token":"TOKEN"},"time":1621307607}
# 此时会获取我的图床的token
https://image.bloged.xyz/api/token?email=邮箱&password=密码
{"code":200,"msg":"success","data":{"token":"TOKEN"},"time":1621307607}
此时返回的是token,而URL连接中多了一串内容,即字典内容,相邻的使用&连接
data
r = requests.request("POST", URL, data = key)
主要函数
requests.get(url, params = None, **kargs)
- url:获取url链接
- params:可选参数,字典或者字节流格式
- **kwars:12个控制访问参数
requests.head(URL,**kwargs)
- url:链接
- **kwars:13个控制访问参数
requests.post(url, data = None, json = None, **kwargs)
- url:链接
- **kwars:11个控制访问参数
requests.put(url, data, **kwargs)
requests.patch(url, data = None, **kwargs)
requests.delete(url, **kwargs)
robots协议
全称:robots exclusion standard 网络爬虫排除标准,告知哪些资源可以爬取,形式为再网站目录下放一个robots.txt文件
Disallow不允许
# *代表所有,allow代表允许,disallow代表不允许,/代表根目录
User-agent:xxxx
Disallow:xxxx
Allow:xxx
如果一个网站没有提供robot.txt,就代表这个网站允许所有爬虫,类人行为可以不遵守此协议
自定义UA访问
import requests
UA = {
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36"}
r = requests.get("https://ie.icoa.cn/", headers = UA)
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
print(r.text)
print(r.request.headers)
使用print(r.request.headers)可以查看传递的UA信息
{'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36', 'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate', 'Accept': '*/*', 'Connection': 'keep-alive'}
# 保存在user-agent中
agent,代理人,媒介,ˈājənt
关键字提交接口
使用params参数传递字典信息,其中url后会自动追加?键 = 值
import requests
keyword = input()
key = {"wd": keyword}
UA = {
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36"}
r = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com/s", headers=UA, params=key)
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
print(r.text)
print(r.request.headers)
print("---------------")
print(r.url)
网络资源的爬取和存储
- 需要资源的URL
- 使用
r.content获取二进制文件,使用文件以二进制形式进行存储
import requests
# 获取百度搜索主页图片
file = open("D:\\VM\\abc.png", "wb")
r = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com/img/PCtm_d9c8750bed0b3c7d089fa7d55720d6cf.png")
print(r.status_code)
file.write(r.content)
也可以使用网页中原有元素的文件名
import requests
r = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com/img/PCtm_d9c8750bed0b3c7d089fa7d55720d6cf.png")
fileName = r.url.split("/")[-1] # 分割字符串获取内容
print("文件名:" + fileName)
file = open("D:\\VM\\" + fileName, "wb")
file.write(r.content)
beautiful soup库
安装库
pip install beautifulsoup4
导入
import bs4
仅使用beautiful soup库
import bs4 from BeautifulSoup
HTML等价于标签树等价于BeautifulSoup库
Beautiful Soup类的使用
可以通过requests访问网页保存其中的内容使用Beautiful Soup类处理,也可以通过打开文件的方式进行处理
BeautifulSoup(文件/文本信息, 解析器字符串)
解析器
| 解析器 | 名称 | 条件 |
|---|---|---|
bs4解析器 | html.parser | 安装bs4库,ˈpärsər解析器 |
lxml的HTML解析器 | lxml | 安装lxml库 |
lxml的XML解析器 | xml | 安装lxml库 |
html5lib的解析器 | html5lib | 安装html5lib |
基本元素
用法
| 元素 | 含义 |
|---|---|
demo.标签名 | HTML标签,最基本的单元,获取标签 |
Name | 标签的名字 |
attrs | 标签的属性,əˈtrɪbjuːt属性 |
string | 标签内非属性字符串,即标签内的内容 |
Comment | 标签内字符串的注释部分,ˈkäment评论,字符串 |
获取网页的某个标签
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.title)
输出内容为整个标签的内容,也包含标签名,只能返回第一个与之匹配的标签
获取标签的名字
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.title)
tag = demo.title
print(tag.name)
此时输出demo中的标签名,此时为title,也可以获取其上一层标签的名字,使用.parent即可
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.title)
tag = demo.title
print(tag.parent.name)
此时输出<title>标签的上一层标签名,即head
<html>
<head>
<title>This is a python demo page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title">
<b>The demo python introduces several python courses.</b>
</p>
<p class="course">Python is a wonderful general-purpose programming language. You can learn Python from novice to professional by tracking the following courses:
<a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">Basic Python</a>
and
<a class="py2" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" id="link2">Advanced Python</a>.
</p>
</body></html>
获取属性值
可以通过.attrs获取属性值的字典
<a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">Basic Python</a>
以上为<a>标签的内容,可以通过attrs将其中的属性值转换为字典
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.a.attrs) # 输出内容
print(demo.a.attrs['class']) # 输出属性值,返回一个列表,因为a中class中可能有多个属性值
获取标签中的内容
可以通过.string进行获取
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.a.string) # 输出标签内的内容,可以跨越多个标签层次
可以跨越多个标签层次,输出最里层的标签内容
遍历
在HTML中,所有的内容都可以画成一棵树,因此,遍历方式有多种,大致分为平行遍历、下行遍历、上行遍历
以上源码中的树为
<html>
/ \
<head> <body>
| / \
<title> <p> <p>
| / \
<b> <a> <a>
下行遍历
| 属性 | 含义 |
|---|---|
.contents | 内容,子节点的列表,将所有的子节点的标签存入列表 |
.children | 子结点的迭代类型,用于循环遍历儿子结点 |
.descendants | 后裔,后代,dɪˈsɛndənts,子孙结点的迭代类型,循环遍历子孙结点 |
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.html.contents)
获取html标签的全部的子结点,输出内容为一个列表,列表中包含标签中的所有内容
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.body.contents)
获取body标签的全部子结点
在树中,可以看出body有两个<p>标签,但直接对body标签的<p>进行操作时,是对第一个<p>进行操作,可以使用列表对其第二个<p>进行访问
其中的回车\n也算是一个子结点
遍历
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
for i in demo.body.contents: # 遍历儿子结点
print(i)
print("------------")
for i in demo.body.children: # 遍历儿子结点
print(i)
print("------------")
for i in demo.body.descendants: # 遍历子孙结点
print(i)
上行遍历
| 属性 | 含义 |
|---|---|
.parent | 结点的父亲标签 |
.parent | 结点的父亲标签的迭代器 |
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
for i in demo.a.parents:
print(i.name)
上行遍历标签的父级,并输出名字
平行遍历
| 属性 | 含义 |
|---|---|
.next_sibling | 按照HTML文本顺序的下一个平行结点标签,兄弟ˈsibliNG |
.previous_sibling | 按照HTML文本顺序的上一个平行结点标签,以前的ˈprēvēəs |
.next_siblings | 迭代类型,后续的平行标签 |
.previous_siblings | 迭代类型,前序的平行标签 |
平行遍历是有条件的,即发生在同一父亲结点下
平行遍历时,下一个被遍历到的不一定是标签 ,也有可能是其他的字符串
可以使用for ...in...进行遍历
让标签格式化输出
即每个标签头独占一行,更便于阅读
使用BeautifulSoup中的.prettify()方法,美化ˈpridəˌfī
用法
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.prettify())
输出内容
<html>
<head>
<title>
This is a python demo page
</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title">
<b>
The demo python introduces several python courses.
</b>
</p>
<p class="course">
Python is a wonderful general-purpose programming language. You can learn Python from novice to professional by tracking the following courses:
<a class="py1" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-268001" id="link1">
Basic Python
</a>
and
<a class="py2" href="http://www.icourse163.org/course/BIT-1001870001" id="link2">
Advanced Python
</a>
.
</p>
</body>
</html>
也可以单独取出其中的标签进行美化
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("https://python123.io/ws/demo.html")
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
print(demo.p.prettify())
该方法也是直接美化第一个出现的标签
信息标记
目前通用的信息标记有三种形式,分别是xml、json、yaml
-
xml为扩展标记语言,与HTML类似,用标签表示各种信息 -
json由有类型的键值对构成 -
yaml由无类型的键值对组成
信息查找
beautifulsoup提供了信息查找的函数
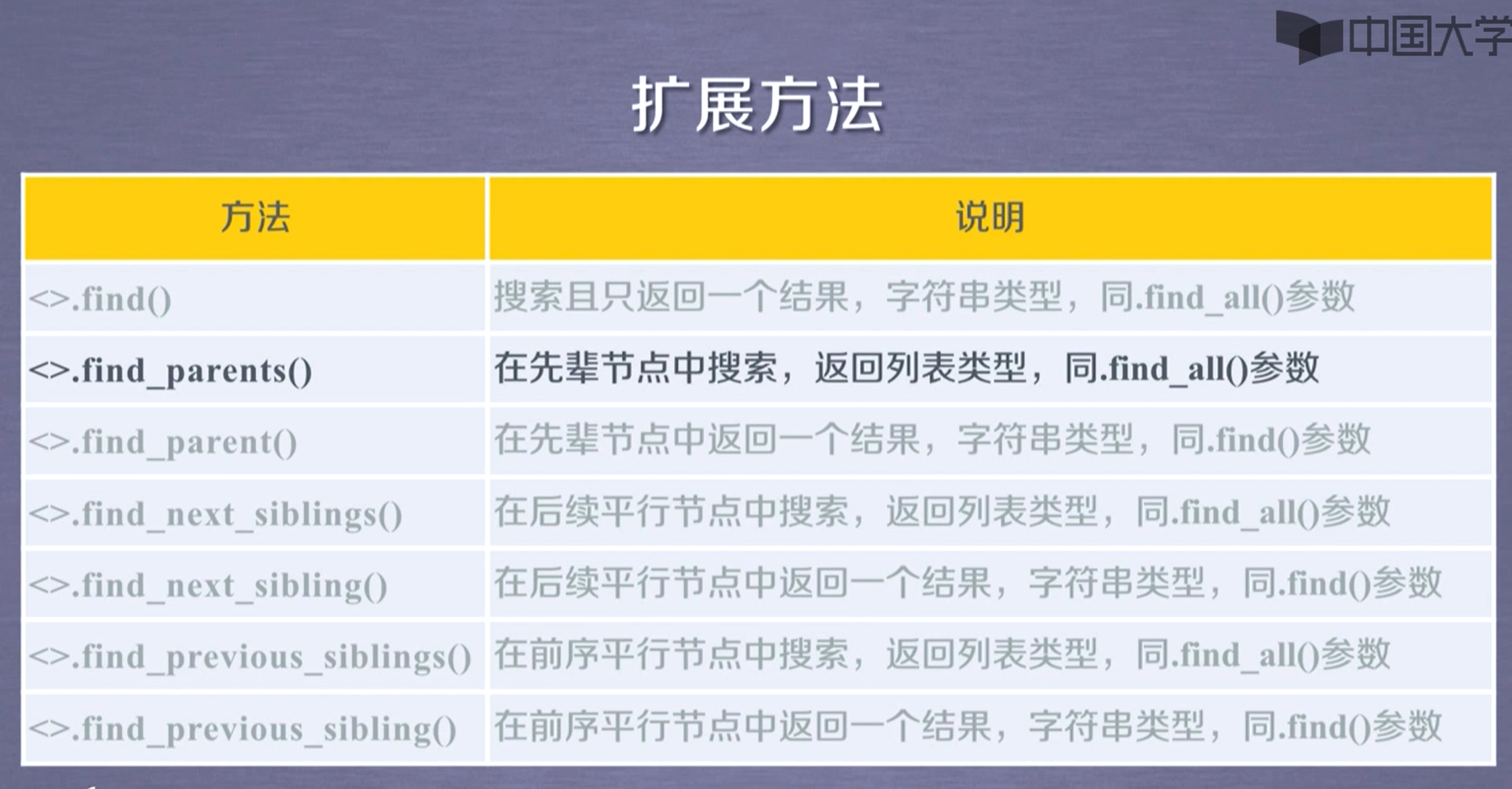
.find_all(name, attrs, recursive, string, id=""),返回列表类型,存储查找结果
如果括号内不写任何参数,返回所有的标签
name为标签名,是字符串格式
attrs返回name标签中含有传递给attrs字符串的选择器属性
id = "字符串"返回含有字符串的字符串的id选择器
recursive是否对其子孙进行查找,为布尔类型,默认为True
string对标签中字符串区域进行查找,将所有含有string的标签的内容全部检索出来
由于该方法特别常用,所以可以省略方法名,例如demo.find_all(id="head")等价于demo(id="head")
例如,获取百度首页的<a>标签
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
# print(demo.p.prettify())
print(demo.find_all("a"))
输出内容为
[<a class="mnav" href="http://news.baidu.com" name="tj_trnews">新闻</a>, <a class="mnav" href="http://www.hao123.com" name="tj_trhao123">hao123</a>, <a class="mnav" href="http://map.baidu.com" name="tj_trmap">地图</a>, <a class="mnav" href="http://v.baidu.com" name="tj_trvideo">视频</a>, <a class="mnav" href="http://tieba.baidu.com" name="tj_trtieba">贴吧</a>, <a class="lb" href="http://www.baidu.com/bdorz/login.gif?login&tpl=mn&u=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com%2f%3fbdorz_come%3d1" name="tj_login">登录</a>, <a class="bri" href="//www.baidu.com/more/" name="tj_briicon" style="display: block;">更多产品</a>, <a href="http://home.baidu.com">关于百度</a>, <a href="http://ir.baidu.com">About Baidu</a>, <a href="http://www.baidu.com/duty/">使用百度前必读</a>, <a class="cp-feedback" href="http://jianyi.baidu.com/">意见反馈</a>]
也可以同时查找多个标签,例如同时查找<a>和<div>标签,即传递的name参数为一个列表
即列表内为需要查找的标签名
print(demo.find_all(["a", "div"]))
如果传递给name的参数为True,则将所有的标签都给返回
将所有的标签名都打印出来,即将所有的标签放入到集合中
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
# print(demo.p.prettify())
s = set()
for i in demo.find_all(True):
s.add(i.name)
for i in s:
print(i)
也可以使用正则表达式作为参数传递进去,只返回含有特定字符的标签
也可以只返回具有同一类属性的标签
import requests # 返回百度首页具有mnav属性的标签
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
for i in demo.find_all(True, "mnav"):
print(i)
# 返回结果
"""
<a class="mnav" href="http://news.baidu.com" name="tj_trnews">新闻</a>
<a class="mnav" href="http://www.hao123.com" name="tj_trhao123">hao123</a>
<a class="mnav" href="http://map.baidu.com" name="tj_trmap">地图</a>
<a class="mnav" href="http://v.baidu.com" name="tj_trvideo">视频</a>
<a class="mnav" href="http://tieba.baidu.com" name="tj_trtieba">贴吧</a>
"""
返回含有某个id属性的标签
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
r = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com")
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
demo = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
for i in demo.find_all(id="head"):
print(i)
Q.E.D.






