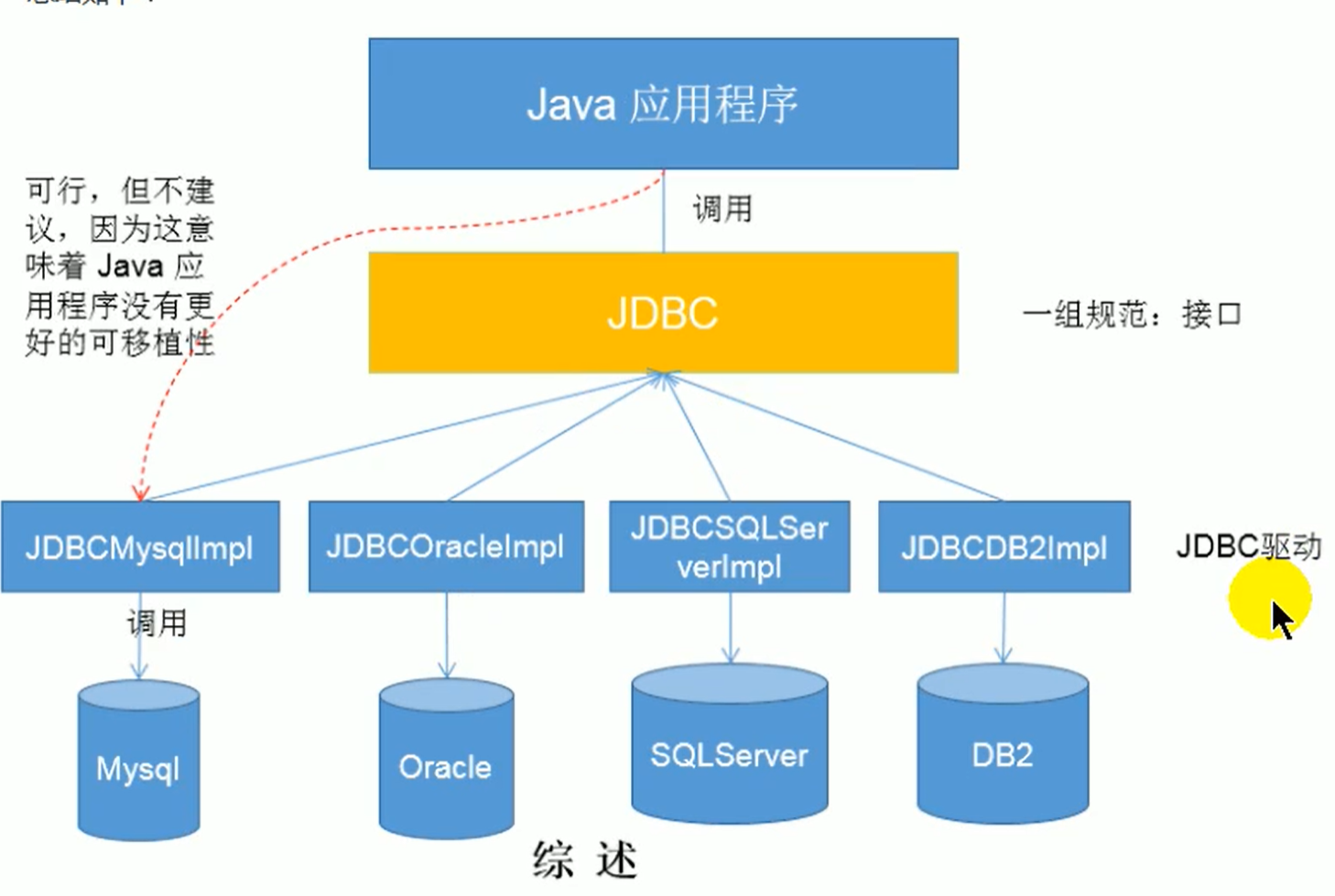
JDBC
全称为Java Database Connectivity,connectivity中文为连通性,读音为käˌnekˈtivədē,是一个独立的数据库管理系统,提供了通用的SQL数据库的存储和公共操作的接口,定义了访问数据库的Java类库,有两个api,分别位于java.sql和javax.sql
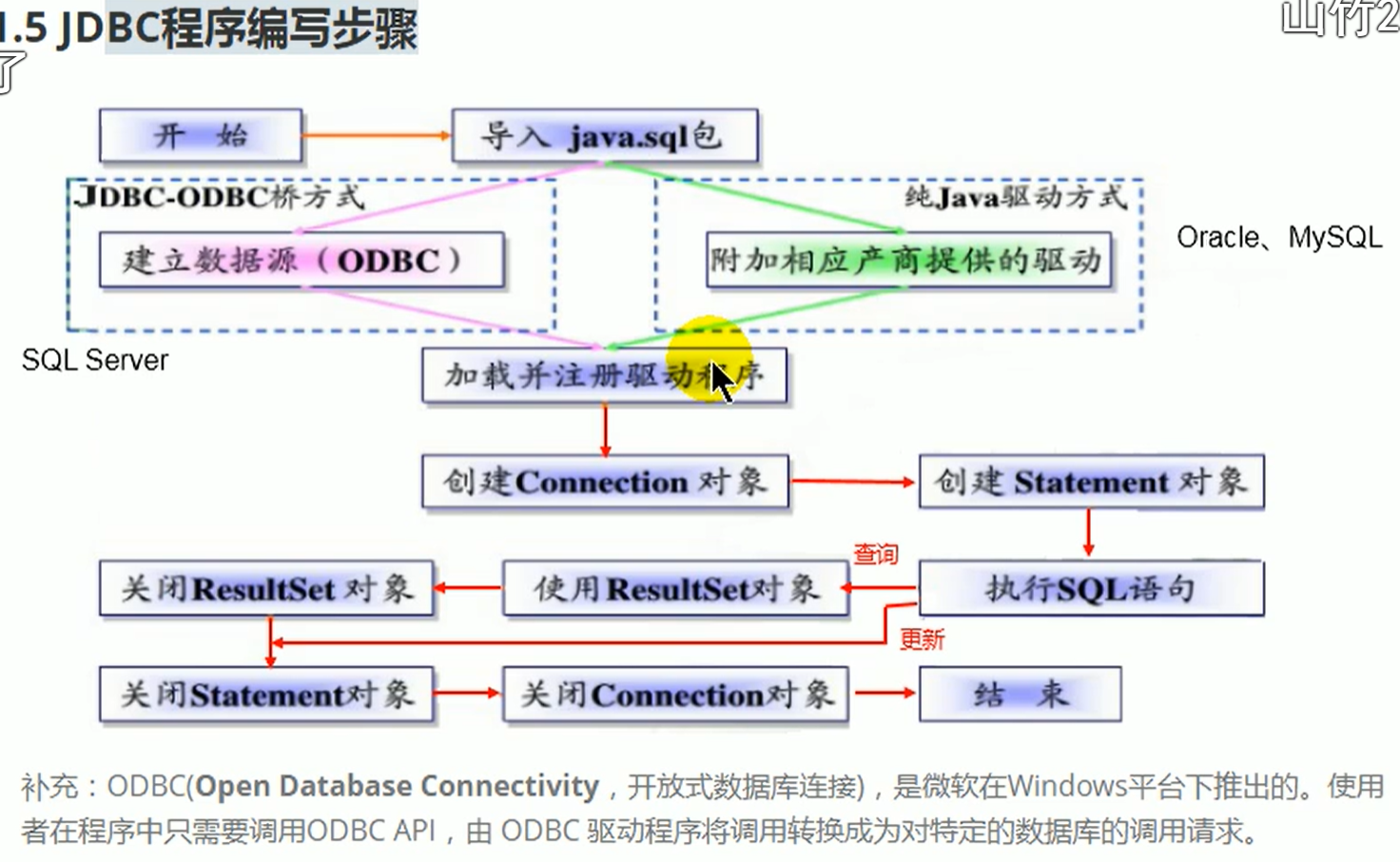
连接数据库
需要驱动,以MySQL为例
-
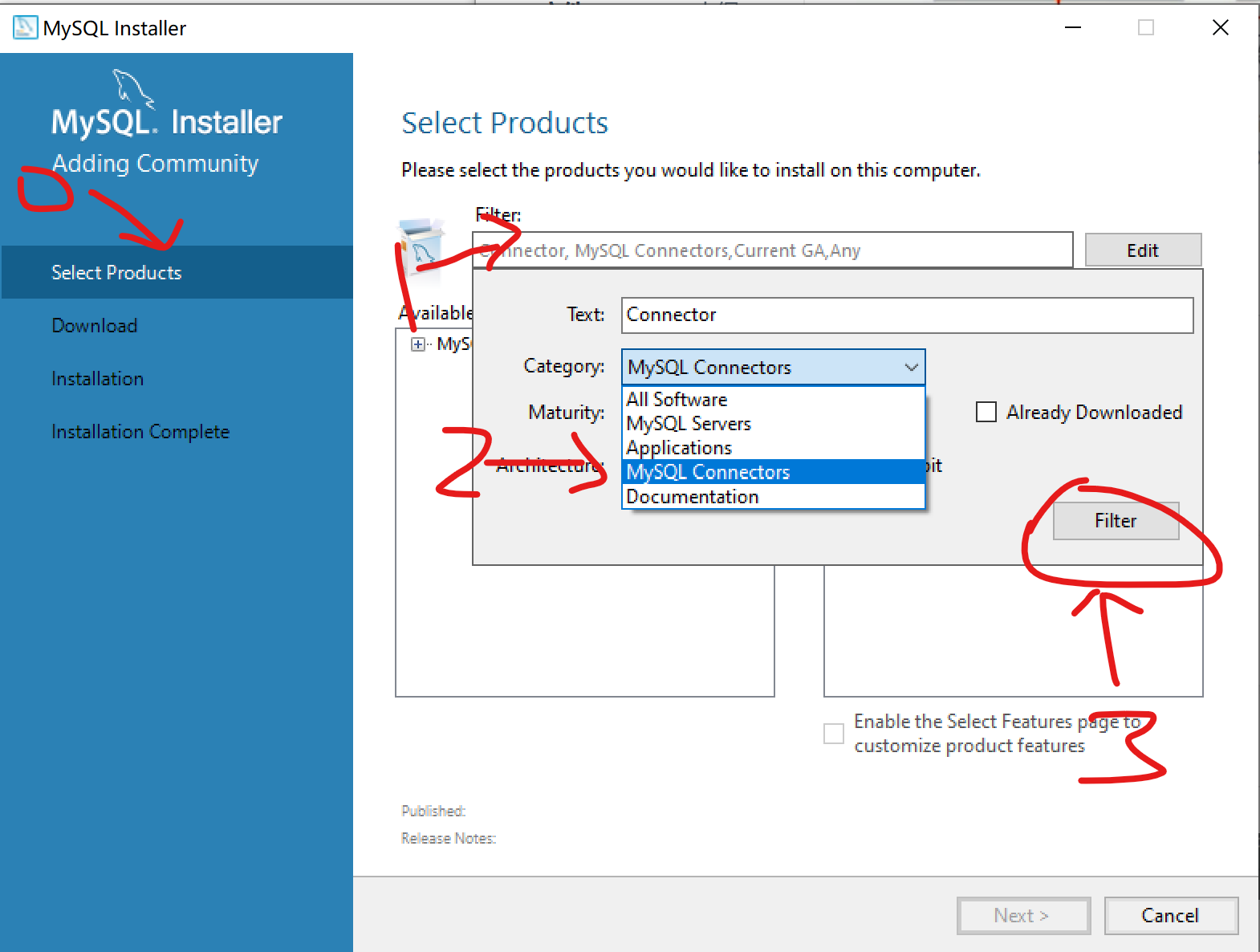
打开MySQL Installer,点击a'd'd
-
选择 选择产品(0),点击编辑框(1),选择category(类别)中的 MySQL连接器(2),点击过滤(3)
-
选择
 ,等待安装成功,默认路径为
,等待安装成功,默认路径为C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\Connector J 8.0 -
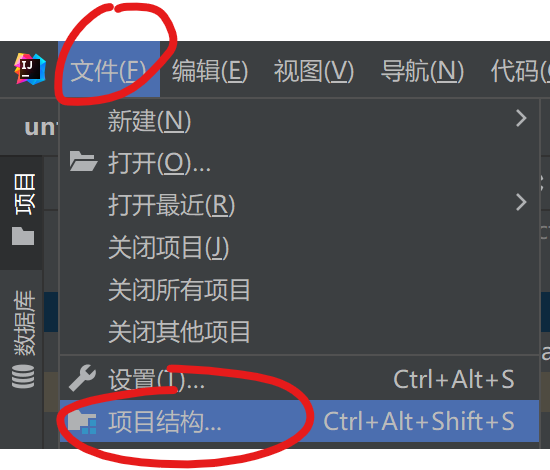
打开idea,导包
-
import java.sql.Driver;
-
-
在项目根目录新建一个文件夹,名字随意,一般为
lib,将下载的.jar文件复制进去 -
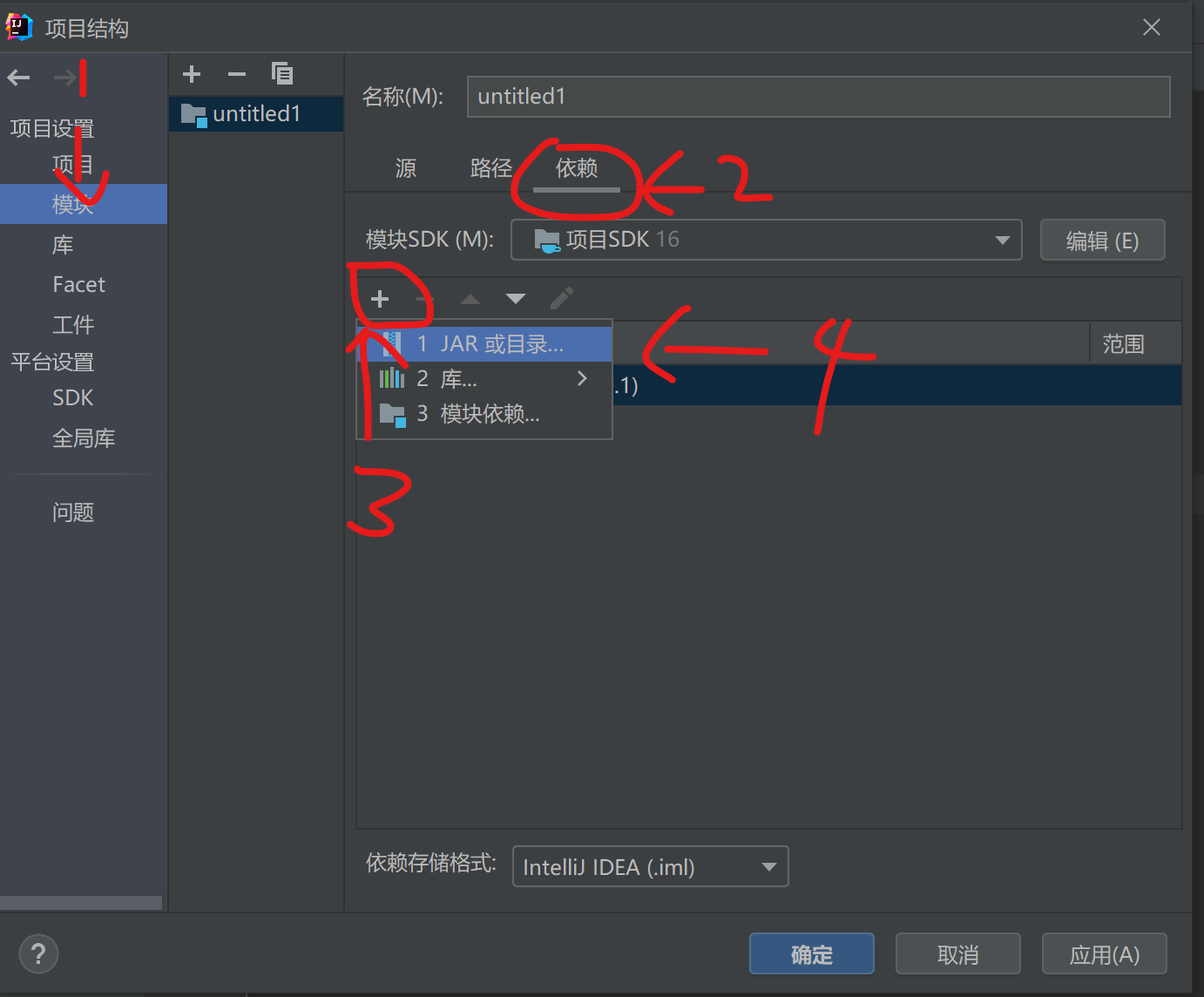
文件-项目文件-项目结构,选择项目结构,点击模块-依赖-加号-jar或目录,选择复制到
lib的文件,点击确定 -
下一步
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver(); 需要抛出异常,异常类型为SQLException完整的连接代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException { //使用drive对象,但com.mysql.jdbc.Driver是第三方类库 Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();//已经弃用 Driver driver = new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver();//新的连接方式 //本地地址为127.0.0.1,也可以写为localhost //默认端口号是3306 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT";//?后为MySQL8必须要写的 //properties中文为特性,是map的古老实现类 Properties info = new Properties();//存储数据库账号和密码 info.setProperty("user", "用户名"); info.setProperty("password", "密码"); Connection connection = driver.connect(url, info);//需要两个参数 System.out.println(connection); }如果输出类似于
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@704a52ec代表连接成功,如果连接不成功,会抛出异常- 获取一个驱动类
- 设置url、账号、密码
- 使用这些信息进行连接数据库,并用信息通过驱动获取一个连接类
3使用反射进行获取
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, SQLException {//需要抛出一堆异常
//通过类的反射获取Class对象
Class c = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//获取这个类空参构造器
Constructor constructor = c.getConstructor();
//使用空参构造器创建一个对象
Driver driver = (Driver) constructor.newInstance();
//本地地址为127.0.0.1,也可以写为localhost
//默认端口号是3306
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT";//?后为MySQL8必须要写的
//properties中文为特性,是map的古老实现类
Properties info = new Properties();//存储数据库账号和密码
info.setProperty("user", "用户名");
info.setProperty("password", "密码");
Connection connection = driver.connect(url, info);//需要两个参数
System.out.println(connection);
}
使用反射的目的就是com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Drive类是自行引入的第三方的api,因为是面向接口编程,需要隐藏第三方的api,所以需要反射
- 通过反射获取一个驱动类
- 设置url、账号、密码
- 使用这些信息进行连接数据库,并用信息通过驱动获取一个连接类
方式3 使用DriverManger替换drive
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, SQLException {
//反射
Class c = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver) c.getConstructor().newInstance();
//提供url、用户名、密码
String url= "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT";
String user = "用户名";
String password = "密码";
// DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);//旧版需要写这条语句,新版无需写,作用是注册驱动
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);//返回连接信息
System.out.println(connection);
}
register中文为注册、寄存器、等级,读音为ˈrejəstər
- 通过反射获取一个驱动类
- 使用驱动管理类,把获取到的驱动注册好,注册驱动时,实现了实例化一个
Driver对象 - 设置url、账号、密码
- 使用这些信息进行在注册好的驱动类连接数据库(注册好的驱动中包含驱动连接信息),并用信息通过驱动获取一个连接类
方法4 方法3的优化
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Class c = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//这一步也可以省略,因为当加载jar包时,jar包已经自动给做了这件事,但不建议删掉,因为其他的数据库可能不会自动执行该语句
String url= "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT";
String user = "用户名";
String password = "密码";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
原理是将com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver类加载到内存中后,会自动执行这个类中的静态方法,静态方法中包含自动注册驱动
- 设置url、账号、密码
- 注册驱动时,自动做好了实例化一个
Driver对象、使用这些信息进行在注册好的驱动类连接数据库(注册好的驱动中包含驱动连接信息),并用信息通过驱动获取一个连接类
方法5 最终版
由于直接将账号、密码写入到程序不是特别安全,可以写一个配置文件,使程序读取配置文件中的账号密码
通常将配置文件放在项目的根目录下的src文件夹内
配置文件的等号两侧不要有空格
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, SQLException {
//读取配置文件
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
//加载配置文件
properties.load(fileInputStream);
//获取相应的值
String url= (String) properties.get("url");
String user = (String) properties.get("user");
String password = (String) properties.get("password");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
- 读取配置文件中的各项信息
- 注册驱动时,自动做好了实例化一个
Driver对象、使用这些信息进行在注册好的驱动类连接数据库(注册好的驱动中包含驱动连接信息),并用信息通过驱动获取一个连接类
增删改查
java.ql包下有3个可以对数据库进行调用的方式 :
statement,中文为陈述,读音为ˈstātmənt,执行静态语句,返回执行SQL后的结果preparedStatement,prepared中文为准备好了、将,读音为prəˈperd,语句被预编译存储在此对象中,可以使用此对象多次高效的执行该语句callableStatement,callable中文为可调用的,读音为ˈkäləb(ə)l,用于执行SQL存储过程
statement
不建议使用,可能有SQL注入的问题,查看问题
preparedStatement
写入后必须执行.excute()方法,否则无法写入!!!!
.executeUpdate()方法为执行并返回执行的条数
插入值(增)
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
String url= "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT";
String user = "账户";
String password = "密码";
//获取连接对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//测试连接情况
System.out.println(connection);
//书写需要执行的sql语句,如果时插入值,values(中的对应的值必须为?),?为占位符,主要解决了sql语句注入的问题
String sql = "insert into user(name, address, phone) values (?, ? ,?)";
//获取一个PreparedStatement实例,并将需要执行的语句传进去
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置值可以使用setXX,对于不同的数据类型都会有不同的XX,有两个参数,参数1为序号,序号为需要设置值的序号,序号取决于表名后的参数列表,序号从1开始,依次进行,参数2为值
//可以使用通用的set,通用的set为setObject,其中值的类型随意
preparedStatement.setString(1, "狗zi");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "beijing");
preparedStatement.setString(3, "1234567");
//执行操作,这一句必须写,不写将不会执行sql语句
preparedStatement.execute();
//需要关闭资源,同样的要抛出异常,可以尝试使用try-catch-finally进行环绕
preparedStatement.close();
connection.close();
}
excute中文为执行,读音为ˈeksəˌkyo͞ot
封装连接、关闭数据库
class ConnectDatabase {
public static Connection connection() throws IOException, SQLException {
// InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
return DriverManager.getConnection((String) properties.get("url"), properties);
}
public static void closeResources(Connection con, PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
ps.close();
con.close();
}
public static void closeResources(Connection con) throws SQLException {
con.close();
}
public static void closeResources(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
ps.close();
}
}
class JDBC5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
Connection connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();
System.out.println(connection);
ConnectDatabase.closeResources(connection);
}
}
由于每次的连接操作都是重复的,可以尝试使用一个静态方法,封装到一个类中
修改(改)
- 连接数据库
- 预编译
SQL语句,返回PreparedStatement实例 - 填充占位符
- 执行
- 关闭资源
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
//连接数据库,使用封装好连接的类
Connection connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();
System.out.println(connection);
//sql语句,需要有占位符
String sql = "update user set name = ? where id = 10";
//预编译sql语句
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置值,写法与插入值的setXXX方法一致,参数1为下标,从1开始,参数2为值
preparedStatement.setString(1, "大狗");
//执行
preparedStatement.execute();
//关闭资源
ConnectDatabase.closeResources(connection,preparedStatement);
}
删除操作与前边的插入操作、更新值的操作一致,如果想要删除整张表,可以不用写占位符,即不需要写?
通用的增删改
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
String sql = "delete from user where name like ?";//测试删除操作
update(sql, "%狗%");//调用尝试
}
public static void update(String sql, Object ...obj) throws SQLException, IOException {//通用的增删改的方法,使用的是可变形参,格式为类型 ...变量名,相当于一个前边类型的数组,第一个参数为SQL语句,第二个参数为填充占位符的相关数据
Connection connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();//连接数据库,基于封装连接的静态方法
System.out.println(connection);//测试是否连接成功
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//预编译sql语句
for (int i = 0; i < obj.length; i++) {//获取数组的长度
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, obj[i]);//依次填充占位符
}
preparedStatement.execute();//执行
ConnectDatabase.closeResources(connection, preparedStatement);//关闭数据库,基于封装连接的静态方法
}
查
query,中文为询问、质疑,读音为ˈkwirē
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//读取配置文件,连接数据库
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(fileInputStream);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection((String) properties.get("url"), properties);
System.out.println(connection);
String sql = "select * from user";、
//执行sql语句,如果有占位符,还需要setXX方法
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultset = preparedStatement.executeQuery();//该方法会返回结果集,即ResultSet类型
while (resultset.next()){//这里的next相当于迭代器的hasNext和next的结合体 返回boolean类型,具有两者的功能,即能够同时判断是否存在下一个数据和指针自动下移
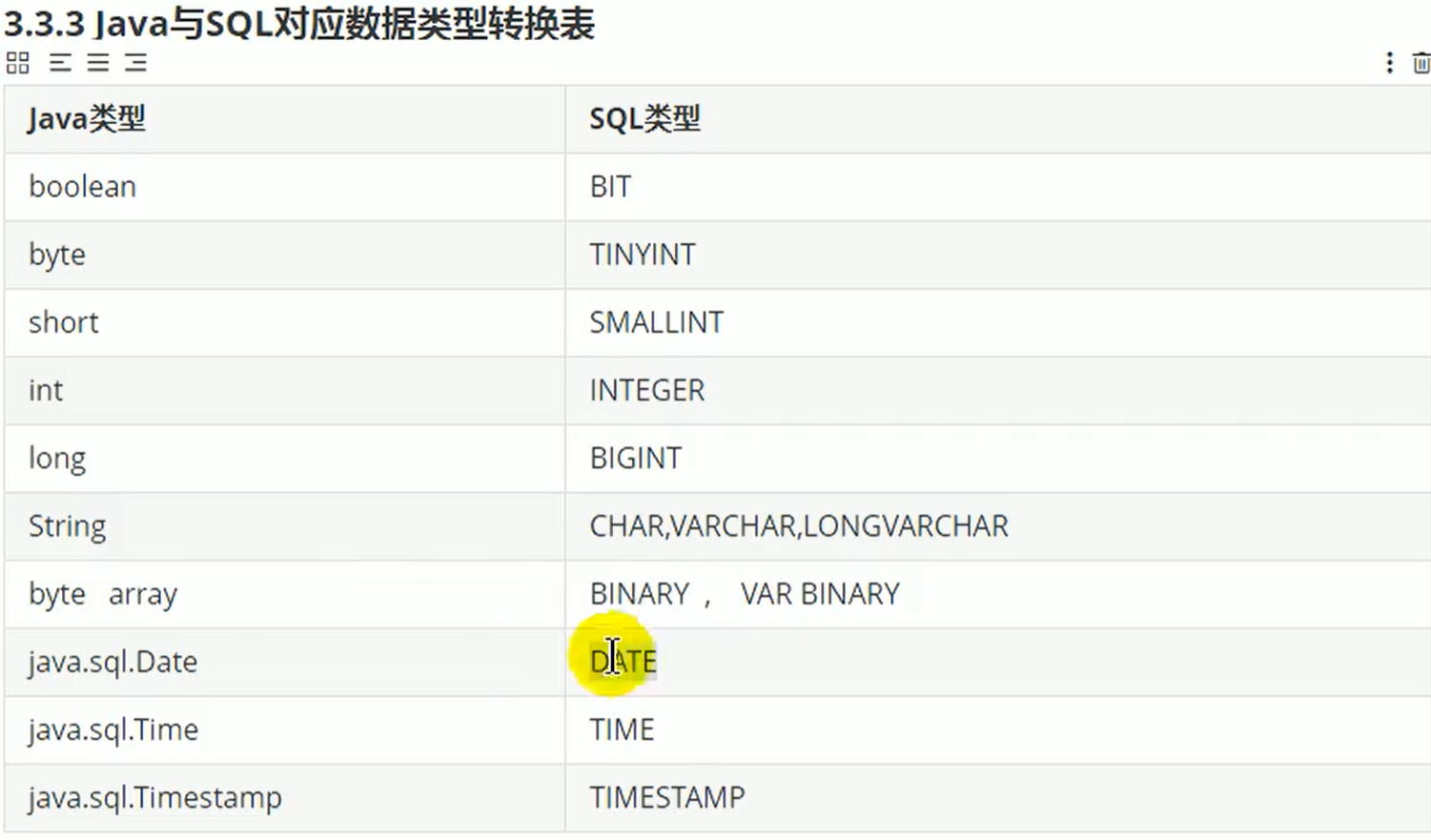
int id = resultset.getInt(1);//获取每个字段的值,需要从1开始,需要类型与数据库原有类型匹配,返回相应的类型,也可以使用Object类型进行获取
String name = resultset.getString(2);//方法的参数也可以写别名(字符串)
String password = resultset.getString(3);
String address = resultset.getString(4);
String phone = resultset.getString(5);
System.out.println("id = " + id + ",name = " + name + ",password = " + password + ",address = " + address + ",phone = " + phone);//挨个输出
}
}
ResultSet类型也是需要关闭的
不定长度的字段名的查询
以上查询仅针对于已知长度的字段名
需要保证有一个针对这个数据库封装好的一个类,类中需要提供好各个属性
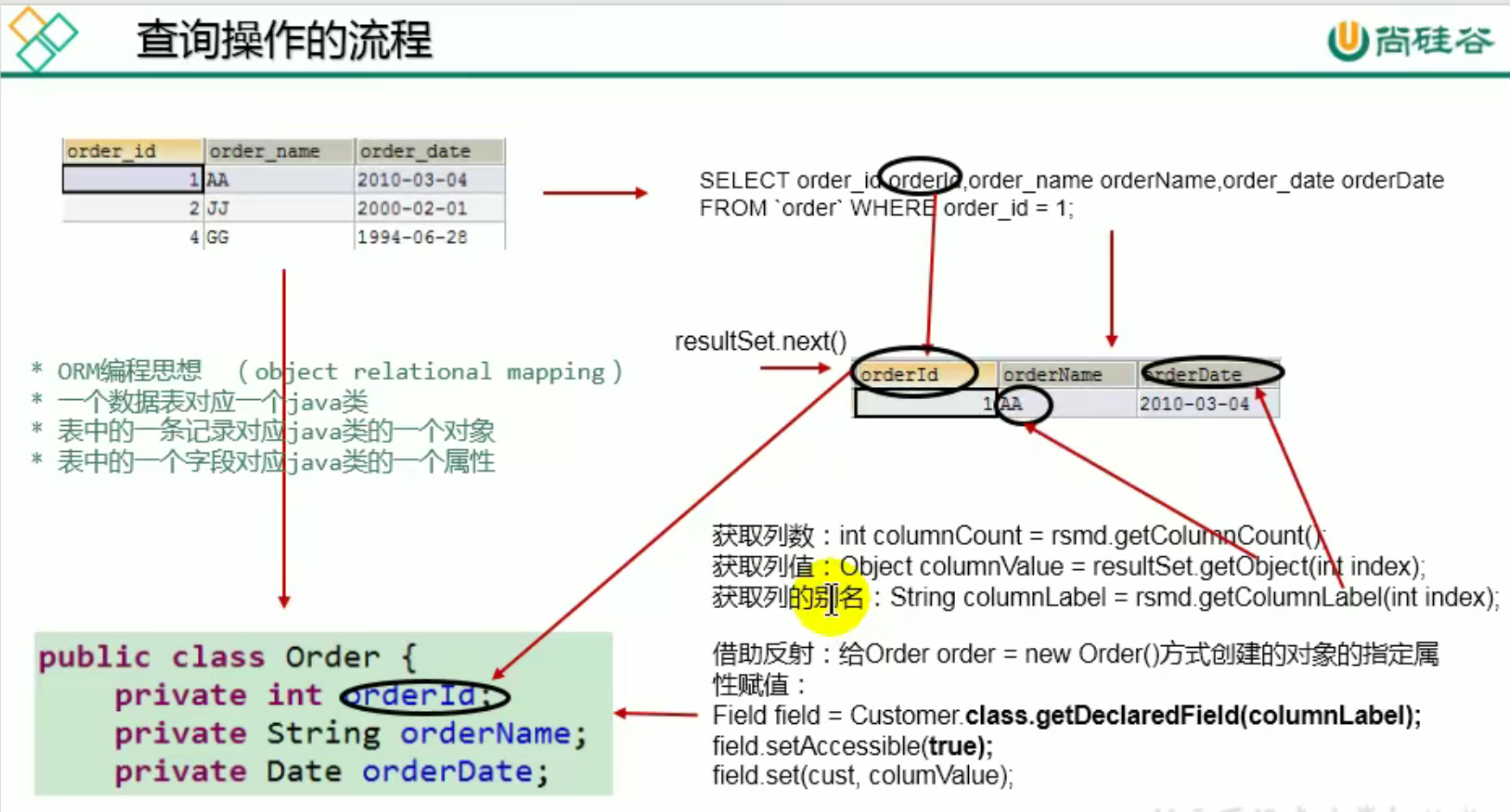
对于未知长度的字段名:
-
执行SQL语句,通过
ResultSet resultSet获取收到的结果集 -
可以通过收到的数据,获取结果集元数据
ResultMetaData resultMetaData = resultSet.getMetaData()- meta,中文为元,读音为
ˈmedə
- meta,中文为元,读音为
-
再通过结果集元数据获取列数
int columnCount = resultMetaData.getColumn()- column,中文为列,读音为
ˈkäləm
- column,中文为列,读音为
-
通过列数得出字段名个数
-
通过一个循环取出每一列,并用一个
Object类型接收- 在循环中,再通过结果集获取每一个结果的字段名,下标从1开始
- 通过获取到的字段名,使用反射给针对数据库封装好的类进行赋值
例如
user表
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | |
| password | varchar(15) | NO | | 123456 | |
| address | varchar(25) | YES | | NULL | |
| phone | varchar(15) | YES | | NULL | |
+----------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
+----+----------+-----------+-----------+-------------+
| id | name | password | address | phone |
+----+----------+-----------+-----------+-------------+
| 1 | 章子怡 | qwerty | Beijing | 13788658672 |
| 2 | 郭富城 | abc123 | HongKong | 15678909898 |
| 3 | 林志颖 | 654321 | Taiwan | 18612124565 |
| 4 | 梁静茹 | 987654367 | malaixiya | 18912340998 |
| 5 | LadyGaGa | 123456 | America | 13012386565 |
+----+----------+-----------+-----------+-------------+
class JDBC7{
public static void query(String sql, Object ...obj) throws Exception, IOException {//对于表user的一个通用的查询方法
//连接数据库
Connection connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();
System.out.println(connection);
//预编译SQL语句
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//填充占位符
for (int i = 0; i < obj.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, obj[i]);
}
//获取结果集
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//获取结果集的元数据
ResultSetMetaData resultSetMetaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//在结果集元数据对象中获取字段的个数
int columnCount = resultSetMetaData.getColumnCount();
//打印字段的个数
System.out.println(columnCount);
//new一个user数组
User[] user = new User[5];
//计数
int count = 0;
while(resultSet.next()){//如果结果集中有记录,指针下移
user[count] = new User();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
//一行中获取下标为i + 1的字段中的具体的值,因为字段从1开始
Object columnValue = resultSet.getObject(i + 1);
//获取下标为i + 1处的字段名
String columnName = resultSetMetaData.getColumnName(i + 1);
//使用反射获取这个类中的字段名的属性,获取属性的前提是首先有一个Class实例,所以需要.class
Field field = User.class.getField(columnName);
//设置权限为true,因为在需要设置的值的这个类中的权限可能为private,所以设置为可写
field.setAccessible(true);
//为其设置值
field.set(user[count], columnValue);
}
count++;
}
//遍历user数组中获取的字段值(可能有多行)
for(var c : user){
System.out.println(c);
}
//关闭资源
ConnectDatabase.closeResources(connection, preparedStatement);
resultSet.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//设置SQL语句的内容
String sql = "select * from user";
//执行查询
query(sql);
}
}
//该类中封装好了user表中的相关属性
class User{
public int id;
public String name, password, address, phone;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", phone='" + phone + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
如果Java类中的命名与数据库中的命名不同,可以给数据库中的相应字段添加别名,一定要与Java类中的属性名相对应,以保持统一
而在之前的代码中,有,该方法获取的是列名,而别名不等于列名!可以使用resultSetMeta.getColumnLabel(下标)获取别名
resultSetMeta.getColumnLabel(下标)方法:
- label中文为标签,读音为:
ˈlābəl - 作用是获取别名
- 如果SQL语句中没有指定别名,则就与
resultSetMeta.getColumnName(下标)方法作用相同,都是获取列名
针对不同表并且通用的查询1
class JDBC8 {
//使用泛型,要求还是必须要一个类接收数据库中的参数,返回一个ArrayList,因为查出来的条数不一定,所以使用ArrayList比较方便
public static <T> ArrayList<T> query(Class<T> tClass, String sql, Object... obj) throws Exception {
//new一个ArrayList
ArrayList<T> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
//连接数据库
Connection connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();
System.out.println(connection);
//预编译SQL语句
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//填充占位符
for (int i = 0; i < obj.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, obj[i]);
}
//执行SQL语句,并获取查询到的条目,得到结果集
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//得到结果集元数据
ResultSetMetaData resultSetMetaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//得到字段数
int columnCount = resultSetMetaData.getColumnCount();
System.out.println("字段数:" + columnCount);
//遍历每条
while (resultSet.next()){
//使用反射动态的实例化一个对象
T element = tClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
//将每行数据挨个写入
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
//获取字段名,如果取了别名,则为别名
String name = resultSetMetaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
//获取值
Object object = resultSet.getObject(i + 1);
//查找属性
Field field = tClass.getField(name);
//属性的权限设为可写入
field.setAccessible(true);
//设置值
field.set(element, object);
}
//添加到ArrayList中
arrayList.add(element);
}
//关闭资源
ConnectDatabase.closeResources(connection, preparedStatement);
resultSet.close();
//返回ArrayList
return arrayList;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String sql = "select * from user";
ArrayList<User> result = query(User.class, sql);
result.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);,sql中的?是为了解决SQL注入问题,如果不写?,直接写相应的值也是可以的,PreparedStatement即使可以拼串,也是解决了解决SQL注入问题,查看,正因为有了预编译,所以才解决了问题
增删改查全套
class JDBC9 {
public static Connection connect() {
System.out.print("账号:");
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String user = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("密码:");
String password = input.nextLine();
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("文件读取失败!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(fileInputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("读取失败");
e.printStackTrace();
}
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection((String) properties.get("url"), user, password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("连接失败,检查账号密码以及配置文件是否正确");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
public static void showMenu() {
System.out.println("----------------------------");
System.out.println("--1----------连接数据库");
System.out.println("--2----------查");
System.out.println("--3----------增删改");
System.out.println("--0----------退出");
System.out.println("****************************");
}
public static <T> ArrayList<T> query(String className, Connection connection, String sql, Object[] obj) throws Exception{
ArrayList<T> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(sql);
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < obj.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, obj[i]);
}
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData resultSetMetaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int columnCount = resultSetMetaData.getColumnCount();
Class tClass = Class.forName(className);
while (resultSet.next()){
T element = (T) tClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
String columnName = resultSetMetaData.getColumnName(i + 1);
Object o = resultSet.getObject(i + 1);
Field field = tClass.getField(columnName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(element, o);
}
arrayList.add(element);
}
return arrayList;
}
public static void update(Connection connection, String sql, Object[] obj) throws SQLException {
System.out.println(sql);
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < obj.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, obj[i]);
}
preparedStatement.execute();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
showMenu();
int flag = input.nextInt();
if (flag == 0) {
break;
} else if (flag == 1) {
connection = connect();
if(connection != null) {
System.out.println("连接成功!");
}else{
throw new Exception("程序退出");
}
} else if (flag == 2) {
Object[] objects = new Object[0];
System.out.print("输入命令,可用?作为占位符:");
input.nextLine();
String sql = input.nextLine();
if(sql.contains("?")){
System.out.print("有占位符,请输入,以空格隔开:");
String placeholder = input.nextLine();
objects = placeholder.split(" ");
}else{
System.out.println("没有占位符");
}
System.out.print("结果需要保存,请输入类名,格式包名.类名:");
String className = input.nextLine();
ArrayList<User> arrayList = null;
try {
arrayList = query(className, connection, sql, objects);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("查询失败,请检查SQL语句以及填充的占位符是否正确");
e.printStackTrace();
}
arrayList.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("查询成功");
} else if (flag == 3) {
Object[] objects = new Object[0];
System.out.print("输入命令,可用?作为占位符:");
input.nextLine();
String sql = input.nextLine();
if(sql.contains("?")){
System.out.print("有占位符,请输入,以空格隔开:");
String placeholder = input.nextLine();
objects = placeholder.split(" ");
}else{
System.out.println("没有占位符");
}
update(connection, sql, objects);
}else{
System.out.println("输入错误");
}
}
}
}
其中,jdbc.properties文件内容为
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库名?&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
操作Blob类型的数据
通过prepatedStatement,可以存储二进制大对象,Statement无法做到
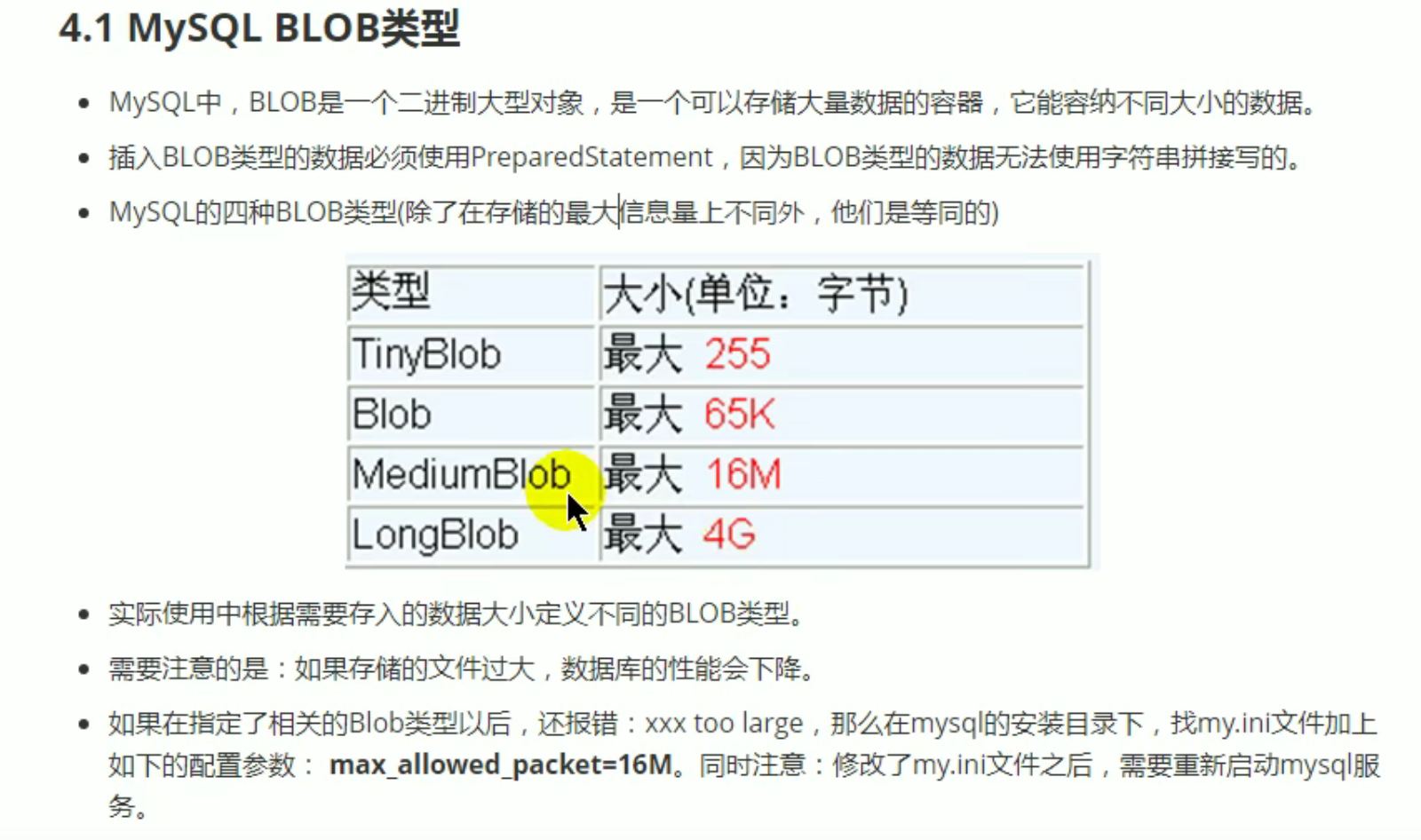
增删改
书写方法与之前的操作类似
String sql = "insert into 表名 values(?????????)";
//预编译sql语句
setBlob(位置, inputStream);
execute();
//例如
preparedStatement.setBlob(4, new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\singx\\OneDrive\\图片\\背景图片\\header-logo.png")));
查询
读取Blob类型使用getBinaryStream(字段名/索引下标),返回InputStream类型
InputStream inputStream = resultSet.getBinaryStream("photo");
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\singx\\Desktop\\111\\1.png"));
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[512];
while((len = (inputStream.read(bytes))) != -1){
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
bufferedOutputStream.close();
inputStream.close();
批量插入数据
update、delete、select天然的具有批量对数据进行处理的能力,可以使用where对数据进行按条件执行
方式1
只预编译SQL语句一次,循环插入数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
Connection connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();
System.out.println(connection);
String sql = "insert into goods(name) values(?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//记录开始时间
System.out.println("开始");
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "name" + i);
preparedStatement.execute();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//记录结束时间
System.out.println(end - start);//执行所用的时间
connection.close();
preparedStatement.close();
}
2万条插入数据,以上执行时间为48305毫秒,效率比较低
方式2 将需要执行的语句攒起来
等达到一定的数量之后再执行SQL语句,利用缓冲的思想
- 攒语句,
PreparedStatement.addBatch() - 执行攒的语句,
PreparedStatement.executeBatch() - 清空已执行的攒的语句,
PreparedStatement.clearBatch()
在JDBC中要想使用批处理,需要在配置文件处添加?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&rewriteBatchedStatements=true
batch,中文是批,批量,读音为baCH
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
Connection connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();
System.out.println(connection);
String sql = "insert into goods(name) values(?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("开始");
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "name" + i);
//攒语句
preparedStatement.addBatch();
if(i % 500 == 0){
//执行攒的语句
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
//清空已执行的攒的语句
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
connection.close();
preparedStatement.close();
}
现在运行时间大概322毫秒
方式3 继续优化批处理
获取数据库连接后(获取PreparedStatement实例之前),将自动提交关闭,等到全部语句执行完之后,再提交
connnction.setAutoCommit(false),关闭自动提交
connection.commit(),最后提交
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
Connection connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();
System.out.println(connection);
String sql = "insert into goods(name) values(?)";
//关闭自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("开始");
for (int i = 0; i < 20000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(1, "name" + i);
//攒语句
preparedStatement.addBatch();
if(i % 500 == 0){
//执行攒的语句
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
//清空已执行的攒的语句
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
//提交
connection.commit();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
connection.close();
preparedStatement.close();
}
事务
set global transaction isolation level 事务隔离级别;
select @@transaction_isolation;
start transaction;
数据一旦提交就不可回滚
自动提交的情况:
- DDL语句
- DML语句,(增删改的默认情况下会提交,获取
PreparedStatement实例之前,将自动提交关闭) - 关闭数据库连接时也会自动提交
关闭自动提交后,调用连接对象的connection.rollback()
---表user_table
+------+----------+---------+
| user | password | balance |
+------+----------+---------+
| AA | 123456 | 1000 |
| BB | 654321 | 1000 |
| CC | abcd | 2000 |
| DD | abcder | 3000 |
+------+----------+---------+
AA向BB转200
class test{
public static void update(Connection connection, String sql, Object... obj) throws SQLException {
System.out.println(sql);
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < obj.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, obj[i]);
}
preparedStatement.execute();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException {
Connection connection = null;
try {//需要同时做的事都写在一个try中
connection = ConnectDatabase.connection();
System.out.println(connection);
//将自动提交关闭
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//AA减200
String sql1 = "update user_table set balance = balance - 200 where user = ?";
//执行语句
update(connection, sql1, "AA");
//手动制造的异常
System.out.println(10 / 0);
//BB加200
String sql2 = "update user_table set balance = balance + 200 where user = ?";
//执行语句
update(connection, sql2, "BB");
} catch (Exception e) {//如果执行完1之后出现了问题,或者执行之前出现了问题,那么就回滚到上次提交的内容
//事务回滚
connection.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
connection.commit();
connection.close();
}
}
}
打开事务(关闭自动)之后还可以打开自动提交,connnction.setAutoCommit(true)

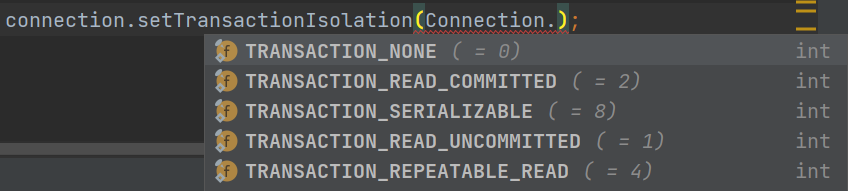
Java设置隔离级别
查询隔离级别:先有一个Connection的实例,调用connection.getTransactionIsolation(),返回int类型
- transaction中文为交易、合同、买卖,读音为
tranˈzakSH(ə)n - isolation,中文为隔离,读音为
ˌīsəˈlāSH(ə)n
//以下在Connection类中声明了常量
//表示不支持事务
finally int TRANSACTION_NONE = 0;
//读未提交,脏读
finally int TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED = 1;
//读已提交,解决了脏读,但有不可重复读和幻读
finally int TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED = 2;
//可重复读,解决了脏读、不可重复读,但有幻读
finally int TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ = 4;
//序列化读
finally int TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE = 8;
设置隔离级别(Connection实例)connection.setTransactionIsolation(值)
可以自定义接口用来对某个表专门定制一个处理的方法
设计思路:设计一个通用的增删改查的类,针对某个表设计一个专用的接口 接口定义一些特定的方法,最后用一个类继承于通用的增删改查的类 实现定义的接口
数据库连接池
使用DriverManager连接数据库的时候,验证账户和密码花费时间较高,如果频繁的连接数据库,会导致效率十分低下,每一次使用数据库时都需要手动的断开,如果在程序异常退出时没有断开数据库,会导致内存泄露,最终导致数据库重启
为解决数据库的连接,引入了数据库连接池
- 基本思想:建立一个缓冲池,在数据库缓冲池中放入一定数量的数据库连接,等需要时只需在缓冲池中取出一个,使用完毕后,再放回去

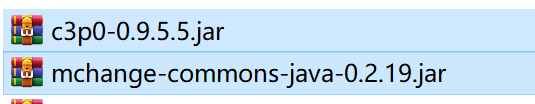
C3P0
项目官网,SourceForge项目仓库,下载可选择带有bin字样的
解压后,将..../lib/c3p0-0.9.5.5.jar和mchange-commons-java-0.2.19.jar导入,并绑定路径
连接数据库
方式1 直接设置密码
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.*;
...
public static void main(String[] args) throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource cpds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
cpds.setDriverClass( "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); //加载jdbc驱动
cpds.setJdbcUrl( "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test" );
cpds.setUser("账号");
cpds.setPassword("密码");
System.out.println(cpds);
}
-
combo中文为组合,读音为ˈkämbō -
pool中文为水池、汇总,读音为po͞ol -
ComboPooledDataSource组合池数据源
方式2 读取配置文件
新建一个配置文件,文件名为c3p0-config.xml
文件内容为
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<c3p0-config>
<!-- 名称 -->
<named-config name="config">
<!-- 获取连接的基本信息-->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">20020327</property>
<!--进行数据库连接池管理的基本信息-->
<!-- 当连接数目不够了,一次性申请的连接数目-->
<property name="acquireIncrement">50</property>
<!--初始化连接容量-->
<property name="initialPoolSize">100</property>
<!-- 维护的最少的池的连接数目-->
<property name="minPoolSize">50</property>
<!-- 最多的连接数,当超过时,需要等待-->
<property name="maxPoolSize">1000</property>
<!-- 最多维护的statement的个数,包括PreparedStatement-->
<property name="maxStatements">50</property>
<!-- 每个连接使用的最多的statement的个数-->
<property name="maxStatementsPerConnection">5</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
将文件放在./src目录下
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//在实例化ComboPooledDataSource对象时,需要将配置文件内设定的名称传入
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("config");
Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
设置初始的数据库连接池的连接数
cpds.setInitialPoolSize(大小)
initial 中文为最初的,读音为iˈniSHəl
获取数据库连接
Connection connection = cpds.getConnection()
增删改查
与之前的方式一样,获取连接后,写相关的方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//实例化一个数据库连接池
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("config");
//获取一个连接
Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
//SQL语句
String sql = "insert into user(name, password, address, phone) values(?, ?, ?, ?)";
String order = "大狗 11111111 beijing 99999999";
//调用之前的方法执行
JDBC9.update(connection, sql, order.split(" "));
}
可以专门用一个类,这个类中有一个静态的变量,这个静态变量是ComnoPooledDataSource实例,如果将该实例放入非静态的方法中,则每次都需要new一个连接池,背离了数据库连接池的原本目的
连接池只需要一个,用的时候直接取出即可
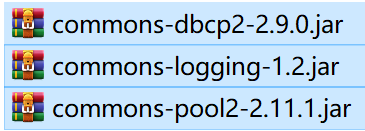
DBCP
依赖于两个jar,分别为commons-Pool和DBCP以及commons-logging
下载二进制文件,解压,将commons-dbcp2-2.9.0.jar和commons-pool2-2.11.1.jar分别导入到./lib中
//导包
import javax.sql.DataSource;
basic 中文为基本的、根本、基、元,读音为ˈbāsik
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//使用空参构造器创建了数据库连接池
BasicDataSource basicDataSource = new BasicDataSource();
//设置基本信息
basicDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
basicDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
basicDataSource.setUsername("root");
basicDataSource.setPassword("20020327");
//获取连接
Connection connection = basicDataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
相关的set方法
首先要有一个BasicDataSource的一个实例
格式为baseDataSource.setXxxx
dbcp连接池常用基本配置属性
1.initialSize :连接池启动时创建的初始化连接数量(默认值为0)
2.maxActive :连接池中可同时连接的最大的连接数(默认值为8,调整为20,高峰单机器在20并发左右,自己根据应用场景定)
3.maxIdle:连接池中最大的空闲的连接数,超过的空闲连接将被释放,如果设置为负数表示不限制(默认为8个,maxIdle不能设置太小,因为假如在高负载的情况下,连接的打开时间比关闭的时间快,会引起连接池中idle的个数 上升超过maxIdle,而造成频繁的连接销毁和创建,类似于jvm参数中的Xmx设置)
4.minIdle:连接池中最小的空闲的连接数,低于这个数量会被创建新的连接(默认为0,调整为5,该参数越接近maxIdle,性能越好,因为连接的创建和销毁,都是需要消耗资源的;但是不能太大,因为在机器很空闲的时候,也会创建低于minidle个数的连接,类似于jvm参数中的Xmn设置)
5.maxWait :最大等待时间,当没有可用连接时,连接池等待连接释放的最大时间,超过该时间限制会抛出异常,如果设置-1表示无限等待(默认为无限,调整为60000ms,避免因线程池不够用,而导致请求被无限制挂起)
6.poolPreparedStatements:开启池的prepared(默认是false,未调整,经过测试,开启后的性能没有关闭的好。)
7.maxOpenPreparedStatements:开启池的prepared 后的同时最大连接数(默认无限制,同上,未配置)
8.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis :连接池中连接,在时间段内一直空闲, 被逐出连接池的时间
9.removeAbandonedTimeout :超过时间限制,回收没有用(废弃)的连接(默认为 300秒,调整为180)
10.removeAbandoned :超过removeAbandonedTimeout时间后,是否进 行没用连接(废弃)的回收(默认为false,调整为true)
使用配置文件进行连接数据库
需要一个Properties文件,基本格式,idea默认读取位置依然是项目下
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
username=账号
password=密码
#其他属性
#比如设置默认大小
initialSize=大小
连接
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties properties = new Properties();
//读取配置文件
properties.load(new FileInputStream("dbcp.properties"));
//通过配置文件实例化一个BasicDataSource对象
BasicDataSource basicDataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
//获取连接
Connection connection = basicDataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
再通过connection的相关方法获取PreparedStatement进行操作
如果设计专用类用来连接数据库时,因为是数据库连接池,所以要将BasicDataSource放入一个静态的代码块中,因为有多个语句,静态代码块中不能抛出异常,需要使用try-catch环绕
//专门的数据库连接池的类
class JDBC14{
public static Connection connection = null;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("dbcp.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
BasicDataSource basicDataSource = null;
try {
basicDataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
connection = basicDataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
return connection;
}
}
Druid
德鲁伊
下载地址Druid,下载druid-版本号.jar即可
还是要放在lib目录下,并用项目结构进行绑定
也是DataSource接口的实现类
//所导入的包
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidPooledConnection;
普通方式创建数据库连接池
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setUrl("数据库连接");
druidDataSource.setUsername("用户名");
druidDataSource.setPassword("密码");
//获取Connection实例
DruidPooledConnection connection = druidDataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
DruidDataSource的实例中,有许多.setXxx的方法进行设置各种默认的属性
使用配置文件创建
依然需要一个Properties实例加载配置文件
文件内容的格式为DruidDataSource的实例中,.setXxx的方法去除set后=参数
url=数据库连接
username=用户名
password=密码
创建
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//加载配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("Druid.properties"));
//使用配置文件,获取DataSource实例
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
//h
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
封装到静态方法中
class JDBC16{
public static Connection connection = null;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("Druid.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DataSource dataSource = null;
try {
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
return connection;
}
}
Apache-DBUtils
是apache提供的开源的jdbc工具类库,对jdbc进行了简单的封装,需要jar包,DBUtils
需要commons-dbutils-1.7.jar文件

对JDBC的简单封装,简化工作量
导入的包
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
common,读音ˈkämən,中文为常见的、共同、普通
增删改
- 实例化一个
QueryRunner实例 - 书写SQL语句,需要填充的位置使用
?代替 - 调用这个实例的
update(Connection con, String sql, Object... o)进行填充并执行SQL语句,执行后,返回一个整数,即执行的SQL语句条数
class JDBC16{
public static Connection connection = null;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("Druid.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DataSource dataSource = null;
try {
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection(){
return connection;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取一个连接
Connection connection = getConnection();
//实例化一个QueryRunner
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//书写SQL语句
String sql = "insert into user(name, password, address, phone) values (?, ?, ?, ?)";
//执行语句,并记录执行的语句条数
int count = queryRunner.update(connection, sql, "admin", "555555", "china", "123456");
System.out.println("添加了" + count + "条记录");
}
}
QueryRunner的核心部分代码与前边自己写的几乎一致,只不过健壮性更好
查
使用QueryRunner实例的.query(Connection, ResultSetHandler<T>接口的实现, 可变形参),返回一个泛型<T>,即这个表所对应的一个类
handler 中文为 处理程序、管理者,读音为ˈhandlər
单条结果可以使用ResultSetHandler接口的实现类BeanHandler
需要保证:
- 与表对应的这个类的权限为
public - 需要在类中提供
setter
单条记录:
如果使用该方式进行接收查询到的数据,即使有多条记录,也只会返回第一条
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "select * from user where id = ?";
//BeanHandler类没有空参构造器,需要传入一个类的Class实例
BeanHandler<User> beanHandler = new BeanHandler<>(User.class);
//返回一个泛型,与设置的泛型一致,参数中可以填充占位符
User query = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, beanHandler, 13);
System.out.println(query);
}
package SQL;
public class User {
public int id;
public String name, password, address, phone;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", phone='" + phone + '\'' +
'}';
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public User() {
}
}
多条记录:
使用BeanListHandler,实例化的方法与BeanHandler一样
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "select * from user";
//使用BeanListHandler<T>类
BeanListHandler<User> beanListHandler = new BeanListHandler<>(User.class);
//此时返回的是List<T>
List<User> query = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, beanListHandler);
//遍历输出
query.forEach(System.out::println);
}
也可以用键值对的形式进行存储
需要使用ResultSetHandler<T>接口的另一个实现类MapHandler和MapListHandler
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "select * from user where id = 1";
//实例化
MapHandler mapHandler = new MapHandler();
//默认返回值为Map<String, Object>
Map<String, Object> query = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, mapHandler);
System.out.println(query);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "select * from user";
MapListHandler mapListHandler = new MapListHandler();
//默认返回List<Map<String, Object>>
List<Map<String, Object>> query = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, mapListHandler);
//尝试对数据处理
for (var c : query){
if(c.get("name").equals("郭富城")){
System.out.println(c);
}
}
}
}
定制查询
例如求最大值、行数
scalar,中文为标量,读音为ˈskālər
可以进行特殊操作的查询
需要ScalarHandler类的实例
class JDBC17{
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JDBC16.getConnection();
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "select count(*) from user";
//实例化一个ScalarHandler实例
ScalarHandler<Long> scalarHandler = new ScalarHandler();
long count = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, scalarHandler);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
如果对提供好ResultSetHandler接口的实现类不满意,也可以自行的实现接口
ResultSetHandler<User> resultSetHandler =new ResultSetHandler<User>() {
@Override
public User handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
return null;//如果查询时,使用这个实例,那么此处返回的值就相当于下边的queryRunner.query的返回值
}
};
例子
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//获取连接
Connection connection = JDBC16.getConnection();
//实例化
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//设置SQL语句
String sql = "select * from user where id = ?";
//创建一个匿名的实现类
ResultSetHandler<User> resultSetHandler = new ResultSetHandler<User>() {
@Override
public User handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
User user = null;
//如果存在值
if(rs.next()){
String name = rs.getString("name");
String password = rs.getString("password");
String address = rs.getString("address");
String phone = rs.getString("phone");
int id = rs.getInt("id");
user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setAddress(address);
user.setName(name);
user.setPassword(password);
user.setPhone(phone);
}
return user;//如果查询时,使用这个实例,那么此处返回的值就相当于下边的queryRunner.query的返回值
}
};
User user = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, resultSetHandler, 1);
System.out.println(user);
}
关闭资源
会手动抛出异常
DbUtils.close(connection);
有多个重载,可以关闭:
ConnectionResultSetStatement
也可以使用不会手动抛出异常的方法
DbUtils.closeQuietly(参数)
Q.E.D.